More than just an acronym, STEM & STEAM represents a educational approach that cultivates the critical thinkers, problem-solvers, and innovators our rapidly evolving world demands. By integrating Science, Technology, Engineering, Art, and Mathematics, we equip students with the mindset and skills to tackle real-world challenges, foster creativity, and collaborate effectively. This hands-on, application-focused framework isn’t just about learning disciplines; it’s about sparking innovation and inviting diverse voices to shape the future.
Discover how each discipline—Science, Technology, Engineering, Art, and Math—adds its own spark to innovation.



Understanding the natural world through observation, experimentation, and analysis.
Technology is the application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, serving both industry and daily life.
Engineering is the application of scientific and mathematical principles to design, build, and maintain solutions that solve real-world problems and improve our lives.
Art highlights the importance of merging artistic creativity and innovation with technical subjects to promote holistic learning, stimulate problem-solving, and strengthen critical thinking skills.
The study of numbers, quantities, shapes, and patterns, and their relationships and applications in various contexts.

Fueling Future Innovation STEM and STEAM empower young minds to think critically, create boldly, and solve real-world problems with confidence. By blending technical skills with creativity, these approaches cultivate curiosity, encourage exploration, and ignite the spark that turns today’s learners into tomorrow’s changemakers. And the numbers speak volumes:
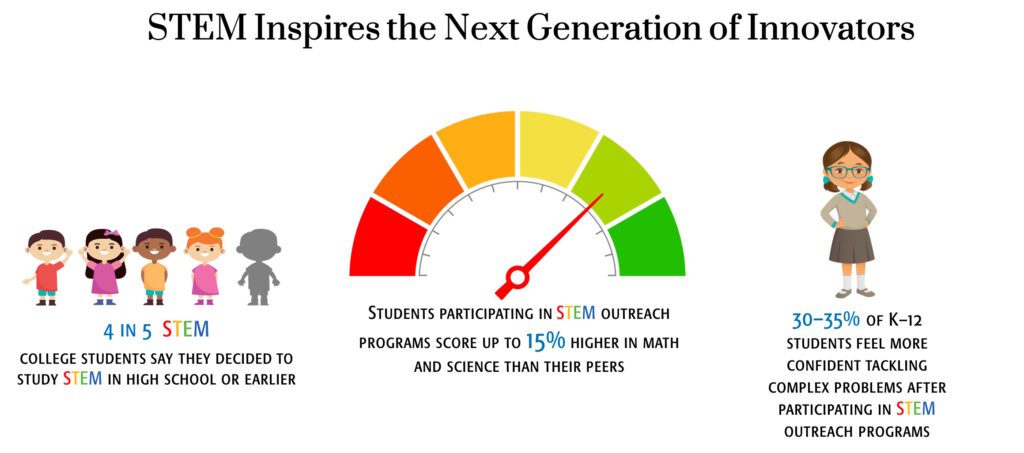

STEM education is vital for equipping students with the critical thinking, problem-solving, and innovative skills essential for success in our rapidly evolving world. By integrating Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics, it fosters curiosity, empowers students to understand and shape their environment, and prepares them for future careers that demand adaptability, creativity, and a deep understanding of how things work. Ultimately, STEM education cultivates the next generation of thinkers, innovators, and leaders ready to tackle the challenges of tomorrow.


STEM isn’t just for the classroom—it’s a lens through which we shape the world. From solving real-world problems to driving innovation, STEM touches every part of our daily lives. The knowledge students build today becomes tomorrow’s breakthroughs in energy, medicine, technology, and beyond.




Science uses investigations and experiments to explain the world around us using evidence. From Astronomers to Zoologists, scientists seek to understand how things work.
Examples of Science Connections to the Real World
- Energy – Science fuels our everyday lives by enabling the harnessing and utilization of various forms of energy, from electricity powering our devices to the combustion processes driving our transportation systems
- Communication: Whether it’s sending a text message, making a phone call, or accessing the internet, communication relies on principles of physics, engineering, and computer science
Environment: Scientific research helps us understand the impact of human activities on the environment and develop strategies to mitigate climate change, reduce pollution, and conserve natural resources

Technology harnesses knowledge to develop innovative devices and tools, enhancing various aspects of life. From the stone tools of prehistoric times to modern robots, advancements in technology have significantly improved communication, transportation, and numerous other fields.
Examples of Technology Connections to Daily Life
- Communication: Technology enables instant communication through various channels such as smartphones, email, social media platforms, and video conferencing tools.
- Information Access: The internet provides access to vast amounts of information on almost any topic imaginable. Search engines, online libraries, and educational platforms allow people to learn, research, and stay informed.
- Healthcare: Technology has revolutionized healthcare delivery, with innovations like telemedicine, wearable health monitors, and electronic health records

Engineering uses math, chemistry, and physics to create new things or to improve products. The goal of an engineer is to solve problems.
Examples of Engineering Connections to Daily Life
- Transportation – Engineers shape the way we move around the world. They ensure that whether we’re driving, flying, cycling, or taking a train, our journeys are safe, comfortable, and efficient. Their innovative thinking shapes the way we move around in the world.
- Healthcare – Medical devices, diagnostic tools, and treatments are all fruits of engineering innovation. Biomedical engineers are the architects behind prosthetics, imaging systems, and medical equipment, all aimed at enhancing healthcare outcomes.
- Energy – Engineers play a crucial role in providing energy for daily life, whether it’s through traditional sources like fossil fuels or renewable sources like solar and wind power. They design power plants, optimize energy distribution, and develop sustainable technologies.
![]()
Mathematics is the backbone for Science, Technology, and Engineering. Its applications across STEM disciplines are crucial for identifying patterns in data. These patterns enable researchers to draw broad conclusions, test relationships, and create models to replicate real-world phenomena.
Examples of Math Connections in Daily Life
- Managing Money – Whether it is balancing your checkbook or figuring out the best price when shopping, math is key when it comes to your money. For example, calculating your interest rate when buying a home or car is an example of utilizing Algebra in the a real world scenario.
- Playing Sports – Athletes use Geometry and Trigonometry to determine the best way to make a goal, hit a ball, or run around a track.
- Home Improvement & Decorating – Algebra and Geometry are used to determine how much paint you need for a project or calculating the area of your flower garden.